前言目前大部分網際網路架構 Cache 已經成為了必可不少的一環。常用的方案有大家熟知的 NoSQL 資料庫(Redis、Memcached),也有大量的程序內快取比如 EhCache 、Guava Cache、Ca
2021-08-17 03:05:07
目前大部分網際網路架構 Cache 已經成為了必可不少的一環。常用的方案有大家熟知的 NoSQL 資料庫(Redis、Memcached),也有大量的程序內快取比如 EhCache 、Guava Cache、Caffeine 等。
本系列文章會選取本地快取和分散式快取(NoSQL)的優秀框架比較他們各自的優缺點、應用場景、項目中的最佳實踐以及原理分析。本文主要針對本地 Cache 的老大哥 Guava Cache 進行介紹和分析。
Guava Cache 通過簡單好用的 Client 可以快速構造出符合需求的 Cache 物件,不需要過多複雜的配置,大多數情況就像構造一個 POJO 一樣的簡單。這裡介紹兩種構造 Cache 物件的方式:CacheLoader 和 Callable
構造 LoadingCache 的關鍵在於實現 load 方法,也就是在需要 訪問的快取項不存在的時候 Cache 會自動呼叫 load 方法將資料載入到 Cache 中。這裡你肯定會想假如有多個執行緒過來訪問這個不存在的快取項怎麼辦,也就是快取的併發問題如何怎麼處理是否需要人工介入,這些在下文中也會介紹到。
除了實現 load 方法之外還可以配置快取相關的一些性質,比如過期載入策略、重新整理策略 。
private static final LoadingCache<String, String> CACHE = CacheBuilder .newBuilder() // 最大容量為 100 超過容量有對應的淘汰機制,下文詳述 .maximumSize(100) // 快取項寫入後多久過期,下文詳述 .expireAfterWrite(60 * 5, TimeUnit.SECONDS) // 快取寫入後多久自動重新整理一次,下文詳述 .refreshAfterWrite(60, TimeUnit.SECONDS) // 創建一個 CacheLoader,load 表示快取不存在的時候載入到快取並返回 .build(new CacheLoader<String, String>() { // 載入快取資料的方法 @Override public String load(String key) { return "cache [" + key + "]"; } });public void getTest() throws Exception { CACHE.get("KEY_25487");}除了在構造 Cache 物件的時候指定 load 方法來載入快取外,我們亦可以在獲取快取項時指定載入快取的方法,並且可以根據使用場景在不同的位置採用不同的載入方式。
比如在某些位置可以通過二級快取載入不存在的快取項,而有些位置則可以直接從 DB 載入快取項。
// 注意返回值是 Cacheprivate static final Cache<String, String> SIMPLE_CACHE = CacheBuilder .newBuilder() .build();public void getTest1() throws Exception { String key = "KEY_25487"; // get 快取項的時候指定 callable 載入快取項 SIMPLE_CACHE.get(key, () -> "cache [" + key + "]");}如果某個快取過期了或者快取項不存在於快取中,而恰巧此此時有大量請求過來請求這個快取項,如果沒有保護機制就會導致大量的執行緒同時請求資料來源載入資料並生成快取項,這就是所謂的 「快取擊穿」 。
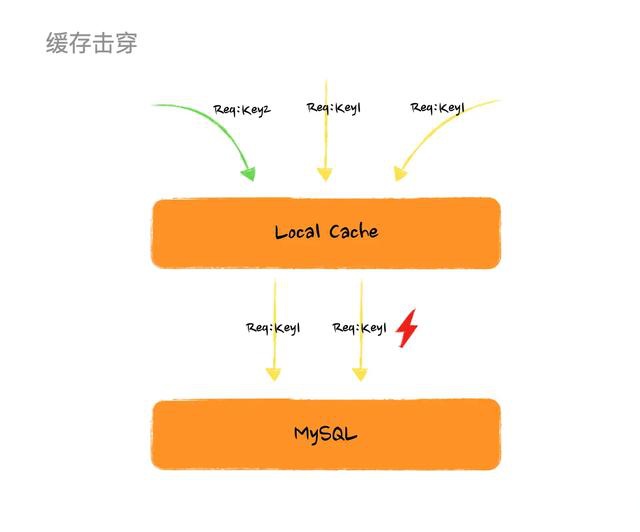
舉個簡單的例子,某個時刻有 100 個請求同時請求 KEY_25487 這個快取項,而不巧這個快取項剛好失效了,那麼這 100 個執行緒(如果有這麼多機器和流量的話)就會同時從 DB 載入這個資料,很可怕的點在於就算某一個執行緒率先獲取到資料生成了快取項,其他的執行緒還是繼續請求 DB 而不會走到快取。

快取擊穿圖例
看到上面這個圖或許你已經有方法解這個問題了,如果多個執行緒過來如果我們 只讓一個執行緒去載入資料生成快取項,其他執行緒等待然後讀取生成好的快取項 豈不是就完美解決。那麼恭喜你在這個問題上,和 Google 工程師的思路是一致的。不過採用這個方案,問題是解了但沒有完全解,後面會說到它的缺陷。
其實 Guava Cache 在 load 的時候做了併發控制,在多個執行緒請求一個不存在或者過期的快取項時保證只有一個執行緒進入 load 方法,其他執行緒等待直到快取項被生成,這樣就避免了大量的執行緒擊穿快取直達 DB 。不過試想下如果有上萬 QPS 同時過來會有大量的執行緒阻塞導致執行緒無法釋放,甚至會出現執行緒池滿的尷尬場景,這也是說為什麼這個方案解了 「快取擊穿」 問題但又沒完全解。
上述機制其實就是 expireAfterWrite/expireAfterAccess 來控制的,如果你配置了過期策略對應的快取項在過期後被訪問就會走上述流程來載入快取項。
快取項的重新整理和載入看起來是相似的,都是讓快取資料處於最新的狀態。區別在於:
由於快取項重新整理的前提是該快取項存在於快取中,那麼快取的重新整理就不用像快取載入的流程一樣讓其他執行緒等待而是允許一個執行緒去資料來源獲取資料,其他執行緒都先返回老值直到非同步執行緒生成了新快取項。
這個方案完美解決了上述遇到的 「快取擊穿」 問題,不過 他的前提是已經生成快取項了 。在實際生產情況下我們可以做 快取預熱 ,提前生成快取項,避免流量洪峰造成的執行緒堆積。
這套機制在 Guava Cache 中是通過 refreshAfterWrite 實現的,在配置重新整理策略後,對應的快取項會按照設定的時間定時重新整理,避免執行緒阻塞的同時保證快取項處於最新狀態。
但他也不是完美的,比如他的限制是快取項已經生成,並且 如果恰巧你運氣不好,大量的快取項同時需要重新整理或者過期, 就會有大量的執行緒請求 DB,這就是常說的 「快取血崩」 。
上面說到快取項大面積失效或者重新整理會導致雪崩,那麼就只能限制訪問 DB 的數量了,位置有三個地方:
所以比較合適的方式是通過新增一個非同步執行緒池非同步重新整理資料,在 Guava Cache 中實現方案是重寫 CacheLoader 的 reload 方法 。
private static final LoadingCache<String, String> ASYNC_CACHE = CacheBuilder.newBuilder() .build( CacheLoader.asyncReloading(new CacheLoader<String, String>() { @Override public String load(String key) { return key; } @Override public ListenableFuture<String> reload(String key, String oldValue) throws Exception { return super.reload(key, oldValue); } }, new ThreadPoolExecutor(5, Integer.MAX_VALUE, 60L, TimeUnit.SECONDS, new SynchronousQueue<>())));先整體看下 Cache 的類結構,下面的這些子類表示了不同的創建方式本質還都是 LocalCache

Cache 類圖
核心程式碼都在 LocalCache 這個檔案中,並且通過這個繼承關係可以看出 Guava Cache 的本質就是 ConcurrentMap。

LocalCache 繼承與實現
在看源碼之前先理一下流程,先理清思路。如果想直接看源碼理解流程可以先跳過這張圖 ~

get 快取資料流程圖
這裡核心理一下 Get 的流程,put 階段比較簡單就不做分析了。
V get(K key, CacheLoader<? super K, V> loader) throws ExecutionException { int hash = hash(checkNotNull(key)); // 根據 hash 獲取對應的 segment 然後從 segment 獲取具體值 return segmentFor(hash).get(key, hash, loader);}V get(K key, int hash, CacheLoader<? super K, V> loader) throws ExecutionException { checkNotNull(key); checkNotNull(loader); try { // count 表示在這個 segment 中存活的項目個數 if (count != 0) { // 獲取 segment 中的元素 (ReferenceEntry) 包含正在 load 的資料 ReferenceEntry<K, V> e = getEntry(key, hash); if (e != null) { long now = map.ticker.read(); // 獲取快取值,如果是 load,invalid,expired 返回 null,同時檢查是否過期了,過期移除並返回 null V value = getLiveValue(e, now); if (value != null) { // 記錄訪問時間 recordRead(e, now); // 記錄快取命中一次 statsCounter.recordHits(1); // 重新整理快取並返回快取值 ,後面展開 return scheduleRefresh(e, key, hash, value, now, loader); } ValueReference<K, V> valueReference = e.getValueReference(); // 如果在 loading 等著 ,後面展開 if (valueReference.isLoading()) { return waitForLoadingValue(e, key, valueReference); } } } // 走到這說明從來沒寫入過值 或者 值為 null 或者 過期(資料還沒做清理),後面展開 return lockedGetOrLoad(key, hash, loader); } catch (ExecutionException ee) { Throwable cause = ee.getCause(); if (cause instanceof Error) { throw new ExecutionError((Error) cause); } else if (cause instanceof RuntimeException) { throw new UncheckedExecutionException(cause); } throw ee; } finally { postReadCleanup(); }}// com.google.common.cache.LocalCache.Segment#scheduleRefreshV scheduleRefresh( ReferenceEntry<K, V> entry, K key, int hash, V oldValue, long now, CacheLoader<? super K, V> loader) { if ( // 配置了重新整理策略 refreshAfterWrite map.refreshes() // 到重新整理時間了 && (now - entry.getWriteTime() > map.refreshNanos) // 沒在 loading && !entry.getValueReference().isLoading()) { // 開始重新整理,下面展開 V newValue = refresh(key, hash, loader, true); if (newValue != null) { return newValue; } } return oldValue;}// com.google.common.cache.LocalCache.Segment#refreshV refresh(K key, int hash, CacheLoader<? super K, V> loader, boolean checkTime) { // 插入 loading 節點 final LoadingValueReference<K, V> loadingValueReference = insertLoadingValueReference(key, hash, checkTime); if (loadingValueReference == null) { return null; } // 非同步重新整理,下面展開 ListenableFuture<V> result = loadAsync(key, hash, loadingValueReference, loader); if (result.isDone()) { try { return Uninterruptibles.getUninterruptibly(result); } catch (Throwable t) { // don't let refresh exceptions propagate; error was already logged } } return null;}// com.google.common.cache.LocalCache.Segment#loadAsyncListenableFuture<V> loadAsync( final K key, final int hash, final LoadingValueReference<K, V> loadingValueReference, CacheLoader<? super K, V> loader) { // 通過 loader 非同步載入資料,下面展開 final ListenableFuture<V> loadingFuture = loadingValueReference.loadFuture(key, loader); loadingFuture.addListener( new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { try { getAndRecordStats(key, hash, loadingValueReference, loadingFuture); } catch (Throwable t) { logger.log(Level.WARNING, "Exception thrown during refresh", t); loadingValueReference.setException(t); } } }, directExecutor()); return loadingFuture;}// com.google.common.cache.LocalCache.LoadingValueReference#loadFuturepublic ListenableFuture<V> loadFuture(K key, CacheLoader<? super K, V> loader) { try { stopwatch.start(); // oldValue 指在寫入 loading 節點前這個位置的值,如果這個位置之前沒有值 oldValue 會被賦值為 UNSET // UNSET.get() 值為 null ,所以這個快取項從來沒有進入快取需要同步 load 具體原因前面提到了,如果通過 // 非同步 reload ,由於沒有老值會導致其他執行緒返回的都是 null V previousValue = oldValue.get(); if (previousValue == null) { V newValue = loader.load(key); return set(newValue) ? futureValue : Futures.immediateFuture(newValue); } // 非同步 load ListenableFuture<V> newValue = loader.reload(key, previousValue); if (newValue == null) { return Futures.immediateFuture(null); } // To avoid a race, make sure the refreshed value is set into loadingValueReference // *before* returning newValue from the cache query. return transform( newValue, new com.google.common.base.Function<V, V>() { @Override public V apply(V newValue) { LoadingValueReference.this.set(newValue); return newValue; } }, directExecutor()); } catch (Throwable t) { ListenableFuture<V> result = setException(t) ? futureValue : fullyFailedFuture(t); if (t instanceof InterruptedException) { Thread.currentThread().interrupt(); } return result; }}V waitForLoadingValue(ReferenceEntry<K, V> e, K key, ValueReference<K, V> valueReference) throws ExecutionException { // 首先你要是一個 loading 節點 if (!valueReference.isLoading()) { throw new AssertionError(); } checkState(!Thread.holdsLock(e), "Recursive load of: %s", key); // don't consider expiration as we're concurrent with loading try { V value = valueReference.waitForValue(); if (value == null) { throw new InvalidCacheLoadException("CacheLoader returned null for key " + key + "."); } // re-read ticker now that loading has completed long now = map.ticker.read(); recordRead(e, now); return value; } finally { statsCounter.recordMisses(1); }}// com.google.common.cache.LocalCache.LoadingValueReference#waitForValuepublic V waitForValue() throws ExecutionException { return getUninterruptibly(futureValue);}// com.google.common.util.concurrent.Uninterruptibles#getUninterruptiblypublic static <V> V getUninterruptibly(Future<V> future) throws ExecutionException { boolean interrupted = false; try { while (true) { try { // hang 住,如果該執行緒被打斷了繼續回去 hang 住等結果,直到有結果返回 return future.get(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { interrupted = true; } } } finally { if (interrupted) { Thread.currentThread().interrupt(); } }}V lockedGetOrLoad(K key, int hash, CacheLoader<? super K, V> loader) throws ExecutionException { ReferenceEntry<K, V> e; ValueReference<K, V> valueReference = null; LoadingValueReference<K, V> loadingValueReference = null; boolean createNewEntry = true; // 要對 segment 寫操作 ,先加鎖 lock(); try { // re-read ticker once inside the lock long now = map.ticker.read(); preWriteCleanup(now); // 這裡基本就是 HashMap 的程式碼,如果沒有 segment 的陣列下標衝突了就拉一個連結串列 int newCount = this.count - 1; AtomicReferenceArray<ReferenceEntry<K, V>> table = this.table; int index = hash & (table.length() - 1); ReferenceEntry<K, V> first = table.get(index); for (e = first; e != null; e = e.getNext()) { K entryKey = e.getKey(); if (e.getHash() == hash && entryKey != null && map.keyEquivalence.equivalent(key, entryKey)) { valueReference = e.getValueReference(); // 如果在載入中 不做任何處理 if (valueReference.isLoading()) { createNewEntry = false; } else { V value = valueReference.get(); // 如果快取項為 null 資料已經被刪除,通知對應的 queue if (value == null) { enqueueNotification( entryKey, hash, value, valueReference.getWeight(), RemovalCause.COLLECTED); // 這個是 double check 如果快取項過期 資料沒被刪除,通知對應的 queue } else if (map.isExpired(e, now)) { // This is a duplicate check, as preWriteCleanup already purged expired // entries, but let's accommodate an incorrect expiration queue. enqueueNotification( entryKey, hash, value, valueReference.getWeight(), RemovalCause.EXPIRED); // 再次看到的時候這個位置有值了直接返回 } else { recordLockedRead(e, now); statsCounter.recordHits(1); return value; } // immediately reuse invalid entries writeQueue.remove(e); accessQueue.remove(e); this.count = newCount; // write-volatile } break; } } // 沒有 loading ,創建一個 loading 節點 if (createNewEntry) { loadingValueReference = new LoadingValueReference<>(); if (e == null) { e = newEntry(key, hash, first); e.setValueReference(loadingValueReference); table.set(index, e); } else { e.setValueReference(loadingValueReference); } } } finally { unlock(); postWriteCleanup(); } if (createNewEntry) { try { // Synchronizes on the entry to allow failing fast when a recursive load is // detected. This may be circumvented when an entry is copied, but will fail fast most // of the time. synchronized (e) { return loadSync(key, hash, loadingValueReference, loader); } } finally { statsCounter.recordMisses(1); } } else { // The entry already exists. Wait for loading. return waitForLoadingValue(e, key, valueReference); }}結合上面圖以及源碼我們發現在整個流程中 GuavaCache 是沒有額外的執行緒去做資料清理和重新整理的,基本都是通過 Get 方法來觸發這些動作 ,減少了設計的複雜性和降低了系統開銷。
簡單回顧下 Get 的流程以及在每個階段做的事情,返回的值。首先判斷快取是否過期然後判斷是否需要重新整理,如果過期了就呼叫 loading 去同步載入資料(其他執行緒阻塞),如果是僅僅需要重新整理呼叫 reloading 非同步載入(其他執行緒返回老值)。
所以如果 refreshTime > expireTime 意味著永遠走不到快取重新整理邏輯,快取重新整理是為了在快取有效期內儘量保證快取資料一致性所以在配置重新整理策略和過期策略時一定保證 refreshTime < expireTime 。
最後關於 Guava Cache 的使用建議 (最佳實踐) :
作者:小梓川呀
連結:https://juejin.cn/post/6996483479965794341
來源:掘金
相關文章
前言目前大部分網際網路架構 Cache 已經成為了必可不少的一環。常用的方案有大家熟知的 NoSQL 資料庫(Redis、Memcached),也有大量的程序內快取比如 EhCache 、Guava Cache、Ca
2021-08-17 03:05:07
在Excel表格中,為了減少資料填寫的錯誤,可以設定資料有有效性,這要怎麼設定呢?1、開啟一個Excel表格,選中需要設定資料有效性的單元格;2、依次點選選單項【資料】-【資料驗證】-【
2021-08-17 03:04:59

早在8月初,iQOO手機官博就爆出將於8月17日釋出iQOO 8系列的訊息,隨後也陸陸續續公佈了很多關於iQOO 8細節的資訊,發稿時截止,除了價格依舊神祕外,其他詳細配置資訊基本齊活了。趁
2021-08-17 03:04:50
工欲善其事必先利其器。工業軟體是晶片及當下工業製造領域的頭部環節,也被稱為人類基礎學科。按照產品形態用途不同,工業軟體可以進一步分為研發設計軟體、資訊管理軟體、嵌入
2021-08-17 03:04:40

隨著全球晶片大缺貨,各大晶圓廠都在想辦法努力提升產能,畢竟有產能就能夠賺大錢。而在提升產能的辦法上,有些企業像中芯國際、臺積電這樣,不斷的自己搞建設擴產能。而有的企業則
2021-08-17 03:04:32

按照規則,每2016個區塊,或者大約每2周,位元幣就會重新設定礦工開採的難度。不出所料,週五凌晨,位元幣程式碼自動使破解一個區塊的難度增加了約7.3%。縱觀位元幣的歷史,這種大幅度
2021-08-17 03:04:21